Table of Contents
What Does It Mean If Your Upper Chest Hurts?
Introduction
A sharp twinge or a dull ache in your upper chest can send shivers down your spine. While heart problems are a concern, upper chest pain can arise from various sources. This article delves into the potential causes of upper chest pain, helping you understand its origin and navigate the situation effectively.
Potential Causes Of Upper Chest Pain
The location and nature of your upper chest pain can offer clues about the underlying cause. Here are some common culprits:
-
Musculoskeletal Issues:
This is a frequent cause. Strained muscles in the chest wall, inflamed cartilage (costochondritis), or injuries to the ribs can trigger sharp pains, especially with movement or deep breaths.
-
Pulmonary (Lung) Problems:
Certain lung conditions can manifest as upper chest pain. Pleurisy (inflammation of the lung lining) can cause sharp, stabbing pain that worsens with breathing. Pneumonia, while sometimes causing upper chest pain, might also present with fever, cough, and shortness of breath.
-
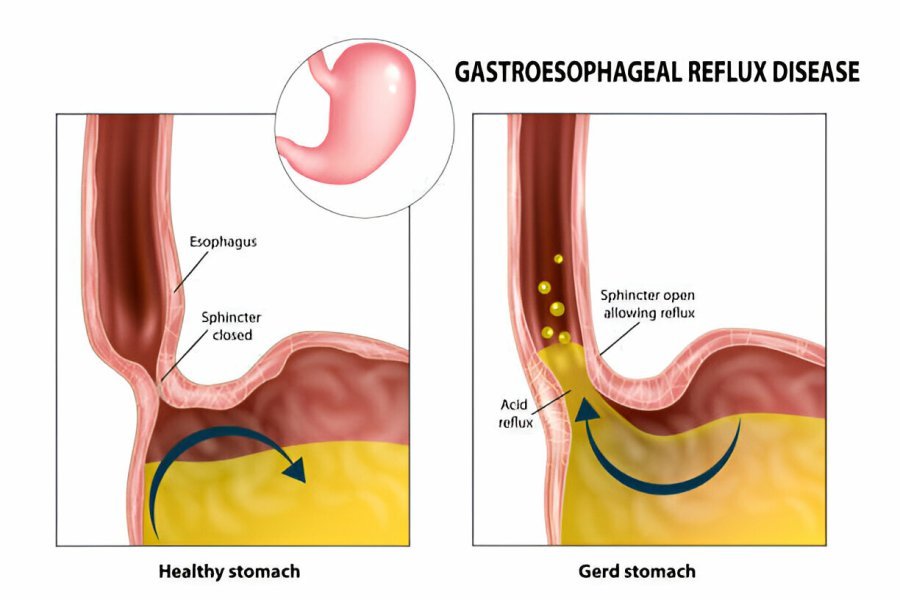
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
Acid reflux, often characterized by heartburn, can mimic heart attack symptoms. The discomfort, a burning sensation in the chest, can radiate to the upper chest, causing tightness or pressure.
-
Anxiety And Panic Attacks:
Anxiety and panic attacks can manifest physically, with upper chest pain being a common symptom. This pain might feel crushing or sharp and often accompanies shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating.
-
Esophageal Issues:
Esophageal spasms, a sudden contraction of the muscular tube connecting your throat to your stomach, can cause sharp chest pain that comes and goes.
FAQs
-
Should I Be Worried About Upper Chest Pain?
While not always serious, upper chest pain can indicate an underlying issue. It’s best to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
-
Can I Treat Upper Chest Pain At Home?
For mild muscle strains or GERD-related pain, over-the-counter pain relievers and antacids might offer relief. However, consult a doctor for persistent pain or concerning symptoms.
-
What Tests Can Diagnose The Cause Of Upper Chest Pain?
A doctor might recommend an EKG (electrocardiogram) to assess heart function, chest X-rays to check for lung problems, or an upper endoscopy to examine the esophagus and stomach.
-
How Can I Prevent Upper Chest Pain?
Maintaining good posture, managing stress, and avoiding triggers like GERD irritants (spicy foods, alcohol) can all help reduce the likelihood of upper chest pain.
Conclusion
Upper chest pain can be concerning, but understanding the various causes empowers you to take appropriate action. If you experience upper chest pain, carefully assess the nature of the pain and any accompanying symptoms. When in doubt, always seek medical attention. Early diagnosis can address the underlying cause and alleviate your discomfort.
References
- Mayo Clinic: Chest Pain https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptom-checker/chest-pain-in-adults-adult/related-factors/itt-20009075
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: What Causes Chest Pain? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470557/
Discover more from Pain Relief Methods
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.