Table of Contents
What Is Non Cardiac Chest Pain?
Introduction
Chest pain can be a frightening experience, often leading to immediate concerns about a heart attack. While heart disease is a serious concern, chest pain can originate from various non-cardiac sources. This article explores non-cardiac chest pain (NCCP), its causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Understanding Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Non-cardiac chest pain refers to chest discomfort that doesn’t stem from the heart or coronary arteries. It’s a prevalent condition, affecting a significant portion of people experiencing chest pain. While NCCP can mimic heart attack symptoms, it arises from different underlying issues.
Causes Of Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
NCCP can have various causes, broadly categorized into four main areas:
-
Musculoskeletal Causes:
Muscles, ribs, and cartilage in the chest wall can become strained or inflamed, causing chest pain. Examples include costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage connecting ribs to the breastbone) and muscle strain from heavy lifting or strenuous exercise.
-
Gastrointestinal Causes:
Conditions affecting the digestive system can manifest as chest pain. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or heartburn, peptic ulcers, and esophageal spasms are common culprits.
-
Pulmonary Causes:
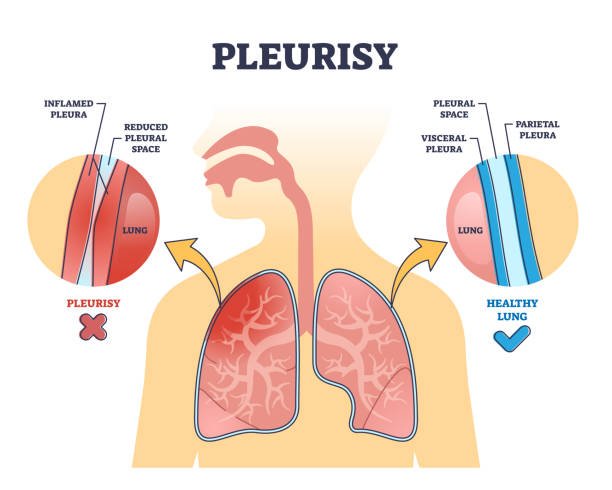
Lung-related issues can also cause chest pain. These include pleurisy (inflammation of the lung lining), pneumonia (lung infection), and pulmonary embolisms (blood clots in the lungs).
-
Psychological Causes:
Anxiety, panic attacks, and stress can manifest as chest pain, often described as tightness or pressure.
Symptoms Of Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
NCCP symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common characteristics include:
-
Chest Pain Location:
NCCP pain can occur anywhere in the chest, not just the left side like heart-related pain.
-
Pain Quality:
NCCP pain can be sharp, stabbing, burning, or a dull ache. It may be constant or come and go.
-
Associated Symptoms:
NCCP may be accompanied by symptoms specific to the underlying cause. For example, GERD can cause heartburn and indigestion, while pleurisy may cause sharp pain that worsens with deep breaths or coughing.
Diagnosing Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Diagnosing NCCP usually involves a comprehensive evaluation by a doctor. This may include:
-
Medical History Review:
Discussing your symptoms, risk factors, and any past medical conditions.
-
Physical Examination:
The doctor will listen to your heart and lungs and check for tenderness or swelling in your chest wall.
-
Tests:
Depending on the suspected cause, various tests can be helpful. These may include electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess heart rhythm, chest X-ray to check for lung problems, or blood tests to evaluate for inflammation or other markers.
Treatment For Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Treatment for NCCP depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
-
Musculoskeletal Pain:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, physical therapy, and applying heat or ice packs can help manage pain.

-
Gastrointestinal Pain:
Medications like antacids or proton pump inhibitors can help reduce stomach acid and relieve heartburn or GERD symptoms.
-
Pulmonary Pain:
Treatment depends on the specific lung condition. It may involve antibiotics for pneumonia, medications to thin blood clots for pulmonary embolisms, or medications to manage airway inflammation.
-
Psychological Pain:
Therapy techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and relaxation techniques can be helpful in managing anxiety and stress-related chest pain.
FAQs
-
Is NCCP Dangerous?
NCCP itself is not usually life-threatening. However, it’s important to seek medical attention to diagnose the cause and ensure there’s no underlying serious condition.
-
Can Anxiety Cause Chest Pain?
Absolutely, anxiety and panic attacks can manifest as chest pain, often described as tightness or pressure. Relaxation techniques can help manage this type of chest pain.
-
What If Home Remedies Don’t Relieve My NCCP?
If over-the-counter medications or home remedies like applying heat or ice packs don’t provide relief for your NCCP, consult your doctor. They can further evaluate your condition and recommend a more targeted treatment approach.
-
Can NCCP Lead To Heart Problems In The Future?
While NCCP itself isn’t directly linked to causing heart problems, some underlying conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol, if left untreated, can increase your risk of heart disease in the long run. Early diagnosis and management of these conditions are crucial.
Conclusion
Non-cardiac chest pain, although concerning, can arise from various non-life-threatening causes. By understanding the different types of NCCP, their symptoms, and treatment options, you can feel more empowered when experiencing chest pain. However, remember that early diagnosis is key. If your chest pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek immediate medical attention. A doctor can accurately diagnose the cause and recommend the appropriate treatment plan for a healthier you.
References
- American College of Gastroenterology: Non-Cardiac Chest Pain (NCCP)
- Cleveland Clinic: Noncardiac Chest Pain: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments
Discover more from Pain Relief Methods
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
